This article is a summary of stock trading in China. It explores the factors that caused the Chinese stocks to drop, assesses the impact of rapid policy changes, and considers the risks and potential future of investing in the Chinese stock market.
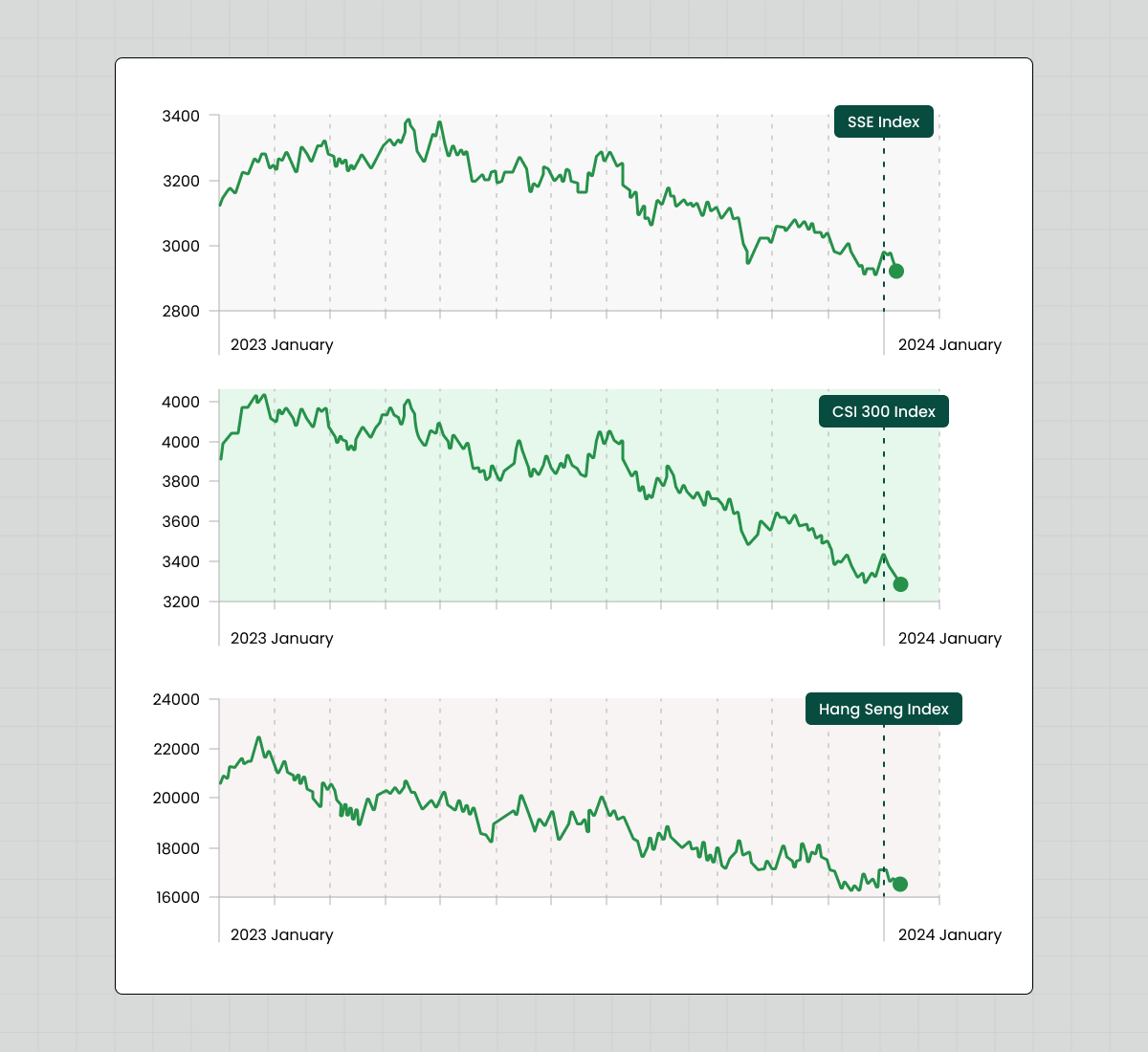
The condition of the Chinese stock market
In early 2021, Chinese stock prices began to decline. The process has intensified over the past year due to several factors. Chief among them was a broad regulatory crackdown on the technology and education sectors, which has wiped out more than $1 trillion in value from major tech companies since November 2020.
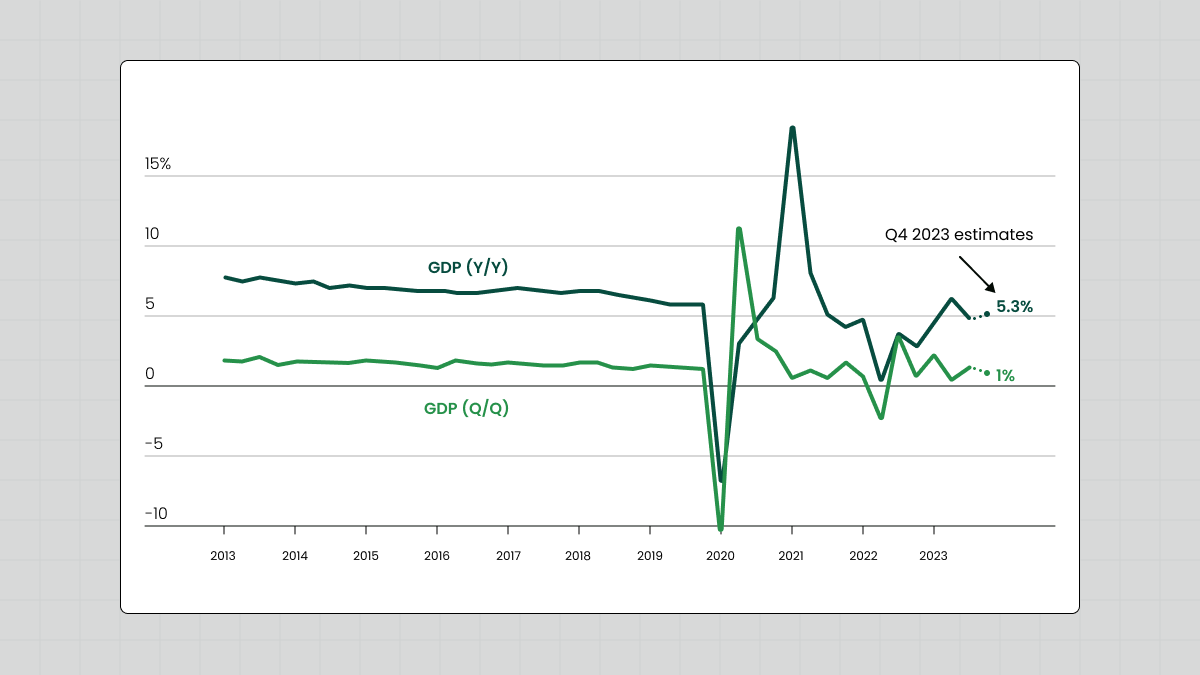
The situation was exacerbated by China's strict zero-coupon policy, which had a significant impact on business confidence, domestic demand, and overall economic productivity. Even after the lockdown was lifted in early 2023, the economic recovery was slow and volatile, impacting corporate profitability and stock performance across sectors.
In addition, geopolitical tensions, particularly with the United States, have increased, leading to restrictive investment measures that have further strained the economic landscape. In 2024, after the Lunar New Year, new regulatory measures were announced under the leadership of the new CSRC chief, Wu Qing, to tighten market practices' scrutiny. However, investor confidence remained low despite these efforts due to continued enforcement against market manipulation and other illegal activities.